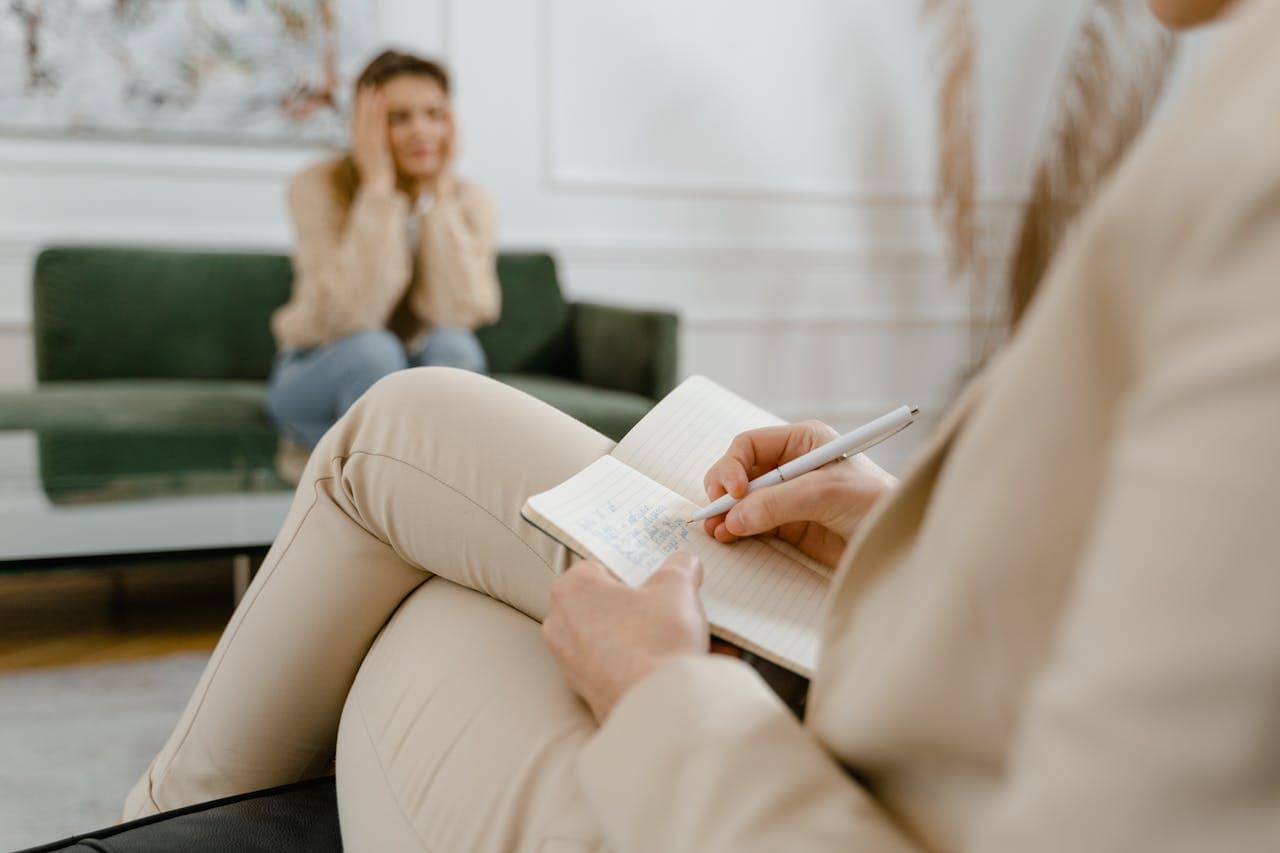
Anxiety disorders affect millions of Americans each year, making them the most common mental health condition in the United States.
Do you ever lie awake at night with racing thoughts? Does your heart pound when facing everyday situations? Many people dismiss their anxiety as "just stress" until it begins controlling their lives, and making them avoid work, skip social events, or struggle with basic daily tasks.
This constant worry goes beyond normal nervousness and can severely impact your quality of life.
Understanding anxiety disorders is the first step toward reclaiming your peace of mind. If anxiety is affecting your life, you deserve to feel better.
Keep reading to discover whether what you're experiencing is normal worry or something that needs professional attention.
Who Experiences Anxiety Disorders?
Anxiety disorders affect people from all walks of life, but certain patterns emerge when we look at who experiences them most frequently. You might be surprised to learn just how common these conditions really are.
Understanding who gets anxiety disorders can help reduce the shame and isolation many people feel.
The Surprising Demographics of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders impact more than 40 million American adults, which is nearly one in five people. These conditions don't discriminate based on age, race, or income level.
Many people develop anxiety during childhood or teenage years, though it can emerge at any stage of life. About one in three adolescents will experience an anxiety disorder. These conditions cut across all demographics, affecting students, professionals, parents, and retirees alike.
Who's Most Vulnerable to Anxiety Disorders?
Several factors can increase your risk of developing an anxiety disorder. Having a family history of anxiety puts you at higher risk, suggesting a genetic component.
Experiencing trauma or significant stress such as abuse, accidents, or loss, also raises your vulnerability. Certain personality traits, such as being naturally shy or having perfectionist tendencies, can make anxiety more likely.
Many people with anxiety also struggle with depression or substance use disorders. Chronic health conditions like heart disease or thyroid problems can trigger or worsen anxiety symptoms.
Understanding these risk factors helps explain why some people develop anxiety while others don't.
What are Anxiety Disorders?
Understanding anxiety disorders begins with recognizing how they differ from everyday worry that everyone experiences.
Anxiety disorders go beyond normal nervousness about specific situations. They create persistent distress that interferes with daily life in significant ways.
Anxiety vs. Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders involve intense, excessive and persistent worry that doesn't match the actual situation. Occasional anxiety is normal when facing challenges at work or making important decisions. But anxiety disorders feature fear that's out of proportion to the real danger.
- Normal anxiety typically fades after the stressful situation passes.
- Anxiety disorders continue for six months or longer and often get worse without treatment.
The key difference lies in how much the anxiety disrupts your daily functioning and quality of life.
The Science Behind Anxiety
Your brain's alarm system triggers anxiety through the fight-or-flight response. This ancient survival mechanism prepares your body to face threats. In anxiety disorders, this system activates too frequently or intensely.
Brain chemistry plays a crucial role, with imbalances in neurotransmitters affecting how you process fear. Physical symptoms like rapid heart rate, sweating, and trembling accompany this heightened state of alertness.
When Anxiety Becomes Dangerous
Untreated anxiety disorders can lead to serious health complications over time. Chronic anxiety increases your risk of heart problems and digestive issues. Many people develop depression alongside their anxiety, creating a difficult cycle. Substance misuse often follows as people try to self-medicate their symptoms.
Anxiety disorders can contribute to suicidal thoughts in severe cases. Anxiety also causes social isolation when people avoid situations that trigger their symptoms. Left unaddressed, anxiety can significantly reduce your quality of life and overall health.
When Does Worry Cross the Line?
Worry becomes an anxiety disorder when it persists long after the stressful situation has passed and begins disrupting your daily life. Many people struggle to recognize when their normal anxiety has crossed into disorder territory.
Understanding this timeline helps you identify when professional help might be necessary.
Timeline of Anxiety: From Occasional Worry to Disorder
Normal anxiety fades once the stressful situation ends. You might feel nervous before a job interview but relax afterward.
Anxiety disorders involve persistent worry that continues for months or years. Situational anxiety becomes a generalized anxiety disorder when worry spreads to multiple areas of life.
Occasional panic attacks transform into panic disorder when you start fearing future attacks.
This progression often happens gradually, making it difficult to notice the shift.
The Red Flags You Shouldn't Ignore
Six months is a key timeframe for generalized anxiety disorder diagnosis. Your anxiety might be problematic if it lasts longer than this.
Another critical sign is when anxiety interferes with daily functioning.
- Avoidance behaviors are major red flags, when you start changing your routine to prevent anxiety.
- Physical symptoms that occur frequently without clear cause also signal a potential disorder.
When to Seek Help?
Ask yourself if your anxiety causes significant distress in your life. Consider whether it affects your work, relationships, or physical health. Mental health professionals use the "distress and impairment" criteria to determine if anxiety warrants treatment.
If your anxiety makes you avoid situations most people handle easily, it's time to seek help.
We recommend seeing a doctor if anxiety interferes with daily activities or causes physical symptoms.
Which Parts of Your Life Get Affected By Anxiety?
Anxiety disorders impact people in specific places and situations throughout their daily lives. You might notice anxiety following you from place to place, affecting different areas of your life in unique ways.
Knowing when and where anxiety shows up most strongly helps you identify patterns and develop targeted strategies.
1. Social Interactions
Social anxiety disorder makes ordinary social situations feel threatening. You might panic at the thought of speaking up in meetings or attending parties.
Simple actions like eating in public or making eye contact can trigger intense fear.
Unlike normal shyness, social anxiety causes significant distress that affects your relationships and opportunities. Many people with social anxiety avoid dating, networking events, or even grocery shopping.
This isolation often worsens the condition over time.
2. Workplace
Workplace anxiety affects millions of professionals across all industries. You might experience panic before presentations or dread team meetings.
Physical symptoms like shaking hands or nausea can interfere with job performance. Some people develop anxiety about email communication or fear making mistakes that could cost their job.
This constant stress leads to burnout, missed promotions, or even job loss.
Managing workplace anxiety often requires specific strategies tailored to your work environment and responsibilities.
3. Home and Family
Anxiety doesn't stop when you close your front door it often follows you home. Family members might unknowingly accommodate your anxiety through avoidance behaviors.
Children can develop anxiety by observing anxious parents.
Separation anxiety affects both kids and adults when loved ones leave the house. Household routines might change to avoid triggering situations. This creates a cycle where anxiety spreads through the entire family system.
Recognizing these patterns helps break the cycle and create healthier home dynamics.
Why Do Anxiety Disorders Develop?
Anxiety disorders develop from a complex mix of biological and environmental factors working together. Understanding these causes helps explain why some people develop anxiety while others don't.
This knowledge also guides effective treatment approaches tailored to your specific needs.
1. The Biological Factors
Your genes significantly influence your risk of developing an anxiety disorder. Research shows anxiety disorders often run in families, suggesting a strong genetic component.
- Brain chemistry plays a crucial role in affecting your fear processing, due to imbalances in neurotransmitters.
- Medical conditions like thyroid problems or heart disease can mimic or worsen anxiety symptoms.
Some people naturally have a more sensitive nervous system that reacts strongly to stress.
2. The Environmental Triggers
- Traumatic experiences, especially during childhood, can trigger anxiety disorders later in life.
- Chronic stress from work, relationships, or financial pressures builds up over time.
- Major life transitions like moving, divorce, or job changes often spark anxiety symptoms.
- Social media exposure also contributes to modern anxiety through constant comparison and information overload.
How to Treat and Manage Anxiety Disorders
Effective treatment for anxiety disorders typically combines therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes to address both symptoms and underlying causes. You don't have to live with constant worry as there are many proven approaches that can help you regain control of your life.
Understanding your treatment options is the first step toward finding relief.
Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) stands as the most effective psychotherapy for anxiety disorders. This structured approach teaches you practical skills to manage anxious thoughts and behaviors. You'll learn to identify negative thought patterns and replace them with more realistic ones.
Exposure therapy gradually introduces you to feared situations in a controlled way. Many people experience significant improvement after 12-16 CBT sessions.
Note: Family therapy can also help when anxiety affects household dynamics.
Therapy gives you tools to handle anxiety long after treatment ends.
Medication Options
Medication often provides essential support alongside therapy for anxiety disorders.
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) like sertraline are typically first-line treatments.
- Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) offer another effective option.
- Beta-blockers can help manage physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat.
- Benzodiazepines provide short-term relief but carry dependency risks.
Note: Never stop medication suddenly without consulting your healthcare provider.
Lifestyle Changes That Make a Real Difference
Daily habits significantly impact your anxiety levels and treatment success. Regular exercise or just 30 minutes of brisk walking most days can reduce anxiety symptoms.
Limiting caffeine and alcohol prevents these substances from worsening your anxiety.
Prioritizing quality sleep creates a stronger foundation for managing anxiety. Mindfulness practices like deep breathing or meditation calm your nervous system. Keeping a worry journal helps identify patterns and triggers.
These changes work best when combined with professional treatment.
Discover how these approaches work together in our guide to Combining Therapy and Medication: Why an Integrated Approach Works.
Conclusion
Understanding anxiety disorders empowers you to take meaningful steps toward recovery and peace of mind. Anxiety disorders affect millions of people, but they don't have to control your life.
Here's what you've learned:
Who experiences anxiety disorders?
Anxiety affects people from all backgrounds, with women twice as likely as men to develop these conditions. Risk factors include family history, trauma exposure, and certain personality traits.
What exactly are anxiety disorders?
These conditions involve intense, excessive worry that persists long after normal stress would fade—interfering with daily life and lasting six months or more.
When does worry cross the line?
Anxiety becomes a disorder when it lasts longer than six months, causes significant distress, and leads to avoidance of everyday situations that most people handle without issue.
Why do anxiety disorders develop?
A combination of biological factors (genetics, brain chemistry) and environmental triggers (trauma, chronic stress) create the perfect storm for anxiety disorders to emerge.
How to treat and manage anxiety?
Evidence-based approaches, including cognitive behavioral therapy, appropriate medication, and lifestyle changes work effectively when tailored to your specific needs.
You deserve to live free from the constant grip of anxiety that disrupts your relationships, work, and daily enjoyment.
Professional support can help you develop coping strategies that work for your unique situation. Many people find significant relief through a combination of therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes tailored to their needs.
Ready to take the next step toward managing your anxiety? Contact our anxiety specialists today for a confidential consultation. Our team has helped thousands of people just like you find effective ways to manage their anxiety.
We'll work with you to create a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific concerns.
With the right support and strategies, you can regain control of your life and find peace of mind.